Understanding Internals of SmokeLoader

Introduction
In this blog we will be discussing about Understanding Internals of SmokeLoader using Ghidra
Analysis
For readers who want to Follow along can get the sample from MalwareBazaar .The sample was first Seen on September 5th 2023 14:12:29 UTC . The sample is 32bit Exe File You can use the tool of your Choice i will be using Ghidra in this blog. The Sample Consists of 3 Stages. In the next sections we will look at each Stages in Detail
Stage 1
The Primary Job of Stage 1 is to Write a new Image to Memory which is the Second Stage
Shellcode Allocation and Calling
The Stage 1 Allocates a Executable Memory in Virtual address space using VirtualAlloc. Writes Shellcode to this address space whose job is to Load the new Image in to Memory
It Calls the Shellcode from Address 40404a If you want to Dump this Shellcode and Understand What it is doing you Can put a Breakpoint on this Location . Stepin to this Call and dump this portion or Follow it in Debugger to Understand What it’s doing
Loading New Image to Memory
The Shellcode first Dynamically Resolves API Call. It uses StackStrings and GetProcAddress to do this
Using the Dynamically Resolved API Calls it Loads the New Image to Memory by Parsing PE Headers. If you have a good Understaing of PE File Formats and it’s offsets the below image will make Sense to you
Some PE File Format offsets i want you take a note is 0x3c and 0x78 . Offset 0x3c is aslo called as e_lfanew it is the File address of new exe header .e_lfanew* + 0x78 gives us the ExportDirectory Virtual Address
After this Shellcode is Comletely executed the New Image will be Loaded in the Memory. You can dump the Second stage from memory Now
Stage 2
Stage 2 is Very Obfuscated Stage with Multiple Anti-Analysis Techniques to Frustrate the Malware Analyst working on it. It Includes Anti-Vm Checks, Encrypted Function code only Decrypted prior to it’s execution, API Hashing etc… The Final Goal of this Stage is to Inject the Third Stage to explorer.exe
Weird Conditional Jumps
This Stage Contains Weird Conditional Jumps as Show in the below image . They are JNZ and JZ jumps with same Destination Address. This is Infact an Unconditional Jump. The Malware is using this technique make it hard for the Disassembler and Decompiler
We can Fix this Easily by finding all the Places with this weird Conditional Jumps and patching it with unconditional Jump.
| |
The Above Python Code does this using Ghidra API After we run this Script all the Weird Conditonal Jumps will be patched to Unconditional jumps and Disasseblers and Decompilera will give us a Better Output. The Below images Shows us the Sample after Execution of th Script
Control Flow Obfuscation
This stage’s Control Flow is Obfuscated with the use of Anti-Debugging Checks
In the Below Image malware uses PEB’s BeingDebugged Field (Offset 0x2) to Check if Process is Being Debugged. If it’s not being Debugged the Offset will contain 0, which is used to Calculate the address where the Control flow is Transfered. If the process is being Debugged the Offset will Contain 1 and will lead to Exception
An other Anti-Deugging Technique it uses is the NtGlobalFlag Field( offset 0x68) in the PEB to Check if it’s Being Debugged. If it’s not being Debugged the Offset will contain 0, which is used to Calculate the address where the Control flow is Transfered. If the process is being Debugged the Offset will Contain 0x70 and will lead to Exception
Encrypted Function Code
One of the most distinctive feature about SmokeLoader is that most of the Function code are in the Encrypted form. They will only be Decrypted just before execution of that code. And will be re-encrypted after that code has been executed
The above image show an Example how the Code look like before Encryption
The decryption_function in the above image is the function which decrypts the Code. It is a normal XOR Decrption. The Function takes three parameters.
- Size of the code to be decrypted
- XOR Key used
- RVA of the Starting of the Code that need to be decrypted. You can use the below function to Decrypt one function at a time
| |
The Below Image Shows the same code after Decryption. The last call to 40131a is wrapper for decryption_function, which will cause the code to be re-encrypted
API Hashing
The Hashing Algorithm used in 2nd Stage is DJB2 hasing Algorithm. In the below image you can see the decompiled code for this. If you are having trouble Understanding this Code i would ask you to read this blog . It Explains in Detail about API Resolving
You can use the below python function to find the values of hashes of the API’s you need.
| |
Checks KeyBoard Layout
Next the malware checks the keyboard layout of the device. If it’s Russian(0x419) or Ukranian(0x422) the malware won’t do any malicious activites. If this is not the case it continues doing it’s Buisness
Previliges Check
The Malware Check if it’s running with Higher Previliges using this API Call’s OpenProcessToken -> GetTokenInformation(TokenIntegrityLabel) -> GetSidSubAuthority It is Checking if the Integrity level is above 0x2000 (SECURITY_MANDATORY_MEDIUM_RID ) If the values greater than 0x2000, it is high integrity. If the user is local admin, but a process was executed normaly, you have the medium integrity Level. If the user clicks run as administrator you would have 0x3000.
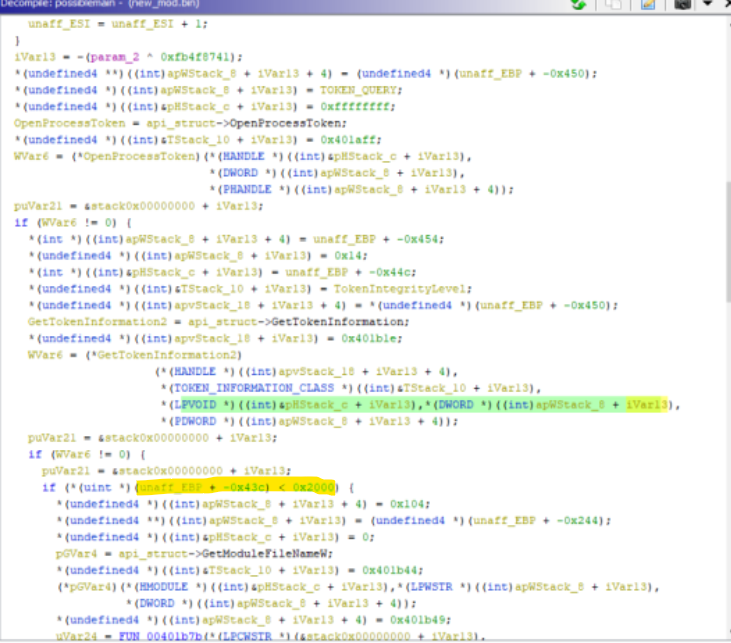
If this is not the Case it will use Run As Administrator Option to get Higher privileges
API Resolving for APIs of NTDLL
The Malware Then Open’s a handle ntdll.dll with shareMode set to 0,Creates a file mapping object for ntdll, Maps a view of this file mapping into the address space of the Malicious process and does API resolving using the Same Hash Algorithm (djb2) in this mapped View. This is to make sure no APIs are being hooked by EDR
Anti-Sandbox, Anti-Emulator and Anti-VM Techniques
The Malware has Multiple Checks to detect if it’s in a VM or sandbox. In the below Image malware is checking if the dlls sbidedll(Sandboxie), aswhook(Avast) and snxhk(Symantec) are mapped into malicious process address space. These DLLs are related to Sandbox solution or Anti-Virus products, another interesting thing to note is that the arguments are stored in the return adress of the function
Another check used by the malware is to check in the Registry Tree for device and drivers if it contains anything related to Virtual machines. It Opens the Registry keys SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\IDE and SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Disk\Enum\SCSI using NtOpenKey and gets and the number and sizes of its subkeys using NtQueryKey
It then uses NtEnumerateKey to get the information about the subkeys and check if this subkeys contains the strings qemu, virtio, vmware, vbox, xen . These strings are related to Emulators and Virtual Machines
The Next check it uses is to detect Emulators . It Checks Current Process’ File path with AFEA.vmt using wcsstr this is a Technique called error-based anti-sandbox check. It is explained in detail by herrcore in this video
Injection of Third Stage using Heavens Gate Technique
The Malware First Checks if it’s running on a 64 bit or 32 bit System by looking at the GS Register because GS is non-zero in Win64 and In a ’true’ 32 bit Windows GS is always zero.. If it’s running on a 64 bit System it uses Heavens Gate technique .“Heaven’s Gate” is a technique used to run a 64-bit code from a 32-bit process, or 32-bit code from a 64-bit process .To know more about this technique I request you to refer this article
Here it is used to run 64-bit code from a 32-bit process for Injection of the Third Stage. If the System only supports 32 bit it Executes the Code shown in the Below Image
The third Stage is injected to explorer.exe. It uses GetShellWindow and GetWindowThreadProcessId to get the process ID of explorer.exe. It then uses NtOpenProcess and NtDublicateObject to create a duplicate handle for explorer.exe. It then creates a section then Maps the same section to malicious process and explorer.exe. Another section is also created and this process is again repeated. The third stage is then written to this section in the malicious Process. Since explorer.exe also has the same section mapped it will also have the third Stage in it’s Memory.
Then RtlCreateUserThread is used to Execute the Malicious third stage from explorer.exe’s address space
if the System supports 64 bit. It Decrpyts the 64 bit code for Injection and uses heaven’s gate technique technique to excecute this. The process of Injection is same for Both. In the below images you can see the 64 bit code which dynamically resolves RtlCreateUserThread API and it is then used to Execute the malicious third stage from explorer.exe’s address space
To get the third stage you can set the GS register to 0 in the debugger at the time of injection, set shareMode to FILE_SHARE_READ (0x00000001) when opening handle to ntdll.dll and defeat all the Anti-Analysis techniques mentioned to get the third Stage in explorer.exe and dump it. You can aslo get the entrypoint of the function if you look at the parameters of the RtlCreateUserThread
Stage 3
The Main objective of this stage is to Decrypt C2 URl Communicate to C2 and Download the Final payload. This stage is also responsible for Persistnace of the Malware
Dynamic API Resolving using API Hashing
Third stage of the malware has a Different set of API resolving . it uses ROL8 hashing you can see the algorithm in the below image
It uses this Hashing Algoritm to resolve APIs in multiple DLLs’ (kernel32, ntdll, user32, advapi32, ole32, winhttp and dnsapi)
You can use the below code to get the Hashes of the APIs used in Third Stage
| |
Encrypted Strings
The Important Strings in the third Stage are Encrypted in a custom rc4 encryption algorithm. The Encrypted string is Stored in the Format of DataSize:Data
When it Comes to the custom rc4 algorithm. The key Stream Generation is Different from the default rc4 algorithm the below image shows the decompiled view of the custom rc4 decryption algorithm
I Have Converted it to python Here is the code to Decrypt the Strings
| |
The Decrypted Strings of the Third Stage can be seen in the Below Image
Analysis Tools Check
This Stage Checks if the system is running Analysis tools by looking at the Process name and Window Class name
In the Below Image you can see the Malicious process Gettting the Name of all the Processes running, Calculates their Hashes using the algorithm used in Stage 3(ROL8 hashing ) and Check it against Hashes of Analysis tools shown in the image below. If they match, that Process is Terminated
There is an Additional Check Which get the Class Name of all top-level windows on the screen. It then Calculates their Hashes using the algorithm used in Stage 3(ROL8 hashing ) and Check it against Hashes of Analysis tools shown in the image below. If they Match, the Process related to that window is Terminated
Previliges Check
The Same Previliges Check done in Stage 2 is done again Stage 3. The Malware Check if it’s running with Higher Prviliges using this API Call’s OpenProcessToken->GetTokenInformation(TokenIntegrityLabel)->GetSidSubAuthority It is Checking if the Integrity level is above 0x2000 (SECURITY_MANDATORY_MEDIUM_RID ) If the values greater than 0x2000, it is high integrity. If the user is local admin, but a process was executed normaly, you have the medium integrity Level. If the user clicks run as administrator you would have 0x3000.
Mutex Check
The Malware Uses the Computer Name and Volume Infromation to a Create a Formatted Data which is used as a Seed to Create an MD5 Hash with these Values. These Values is used in Multiple Places
One of the most important Place these Value used is to Create a Mutex with this name. The Malware Creates a Mutex with this name and After that uses RtlGetLastWin32Error , if the return value is ERROR_ALREADY_EXIST Malware Exits the Thread. This is done by the malware to make sure the malware is run only once in a System
Copy to New Path and use of Zone.Identifier
The Malware Creates a File Path at AppData or Temp . Check if the File running is in this Path. If it is not Running on this path it Delete itself and Copy the File from Curent Location to the File Path Created at AppData or Temp
One Important thing to note here is the Malware Also removes the Alternate Data Stream :Zone.Identifier . It Stores the Data whether the file was downloaded from the Internet. By Doing this System won’t Understand the File was downloaded from Internet
Changing File Attributes and FileTime
After Moving the File to Appdata or Temp . The Files Attribute is Changed to 6 ( FILE_ATTRIBUTE_SYSTEM | FILE_ATTRIBUTE_HIDDEN). This makes the File Hidden and operating system uses a part of, or uses this File exclusively.
Then Malware Chnages the Malicious Files Creation Time , Last Access Time and Last Write Time to the Creation Time , Last Access Time and Last Write Time of advapi32.dll in System Dir. My Assumption for this Technique is that it is trying to not show it’s a New File
Persistance
The Persistance is Achieved by Creating a Scheduled task using ITaskService interface
First it Deletes the Task with Name FireFox Default Browser Agent{MD5 Value Used to Create Mutex} . Then It Sets Author of the task as Current User. Then Trigger of the task is set when the Current User Logins in. The File path of Task is Set to the Malicious File Copied to AppData or Temp And It Finally Registers the task with name FireFox Default Browser Agent{MD5 Value Used to Create Mutex}
C2 Decryption and Communication
The C2 URL’s are Encrypted using the Same Custom rc4 encryption Algorithm used in Stage3. The Data is also Stored in the Same format DataSize:Data. You can use the Same Decryprtion Function mentioned above to decrypt the Strings
Here is the List of C2 URL’s i found in this Malware
The malware then uses the c2 URL with WinHttp Library to Communicate to the C2 server
Since It’s a Loader Based on C2 Response It Loads the Final Payload
Indicators of Compromise
| Type | Indicator | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 5c1735b8154391534f98e6399a2576a572c7fd3c51fa6ecc097434c89053b1f7 | Initial File |
| CnC | hxxp://potunulit[.]org/ | Command and Control |
| CnC | hxxp://hutnilior[.]net/ | Command and Control |
| CnC | hxxp://golilopaster[.]org/ | Command and Control |
| CnC | hxxp://newzelannd66[.]org/ | Command and Control |